The concept of Safety started back in 1939 with the introduction of the seatbelt, however, it took the world three decades to actually accept and adapt to this because many manufacturers thought that putting seatbelts might negatively impact their images. The main thing that changed over the period of time is the speed of the vehicles. The collision resulted in the loss of life and all manufacturers realized the importance of Safety systems. Now they started using the Safety systems as a marketing tool and that is still carried forward to this date. Safety systems have evolved continuously over the period of time and the current generation of vehicles is equipped with a plethora of standard safety systems along with a list of driver aids. Safety systems can be broadly classified into Active Safety Systems and Passive Safety Systems.
Active Safety Features:
These are those safety features that actively prevent the chance of an accident. These are always active in a vehicle right from the moment of ignition and are not usually under the control of the driver with a few exceptions. The following few active safety features are listed below:
- Anti-lock Braking system: This system prevents the locking of the brakes when applied during cornering by the hold and release mechanism. Earlier when the brakes were slammed hard, especially while cornering the tires were locked, as a result, the vehicle skidded. The Anti-Lock braking system allows the disc brakes to be released and grabbed continuously without letting it get stuck as a result it prevents the skidding of the vehicle and helps in high-speed cornering and aids maneuverability. The Anti-lock brakes were a mandatory feature from the year 2000.

- Traction Control System: The traction control system is again an active feature that detects the vehicle’s traction levels using the ABS sensors along with the RPM of each wheel. It is particularly useful in scenarios when the friction on the road is less. It detects which wheel is spinning fast and cuts power to that wheel to provide traction. The only situation in which traction control is not helpful is during offroading.
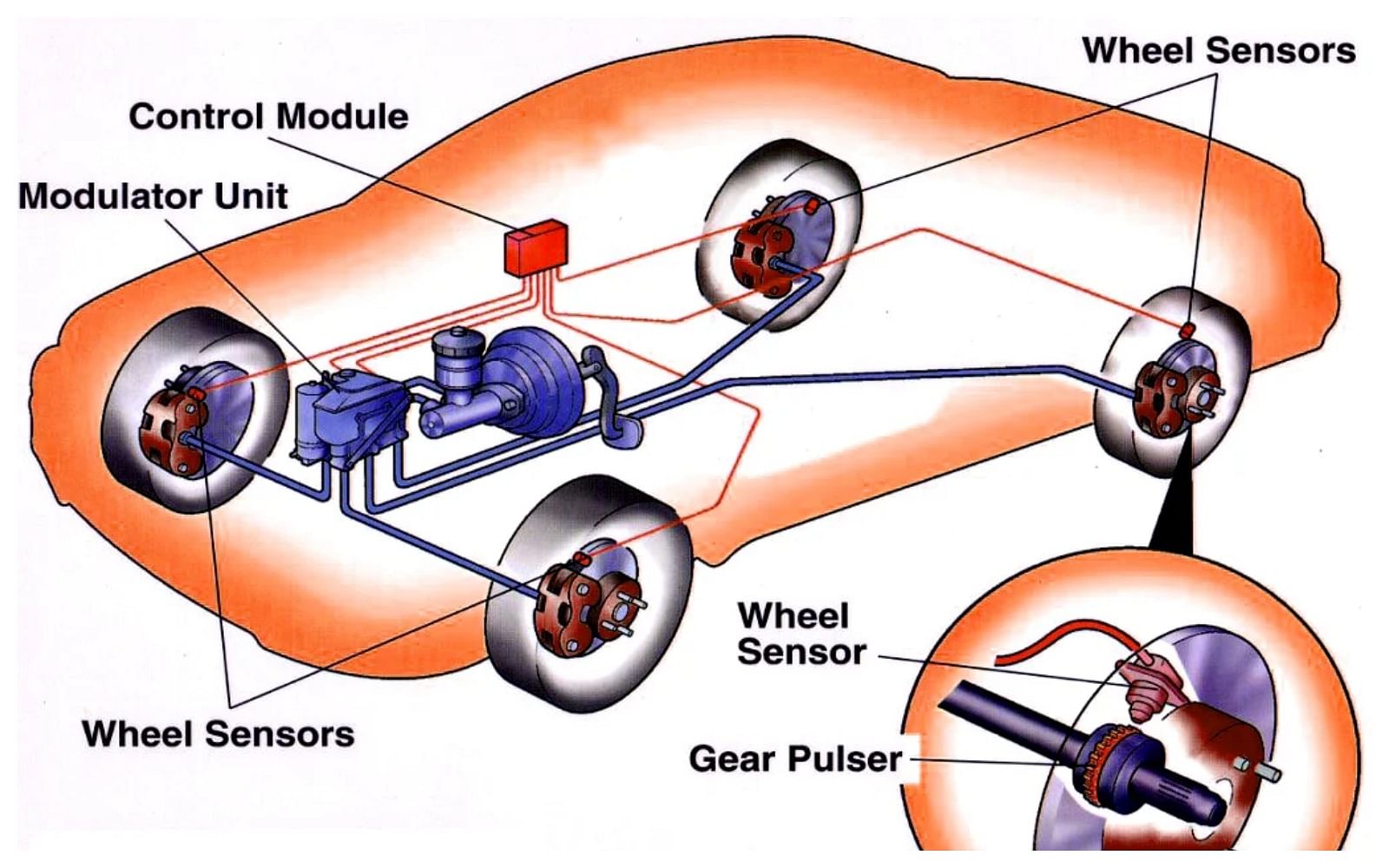
- Electronic Stability Control: This system uses sensors from the ABS and the traction control system to judge whether a vehicle is moving in accordance with the inputs of the driver. This system helps to reduce the lateral motion of the vehicle by extensive use of ABS, a Traction control system, and the four-wheel independent braking system. This feature became mandatory in all passenger vehicles in 2012.

- Electronic brake distribution: This type of system is often present in two-wheelers in which, during an emergency, if one of the brakes is applied the brake power is distributed to both front and rear wheels. This system is also present in four-wheelers and it uses the ABS to divide the brake force.

- Brake Assist: This system measures the input from the driver and the intensity of the input during panic braking scenarios and uses that to electronically alter the braking power via the ABS technology.

- Tire Pressure Monitoring System: This is another active safety system that allows the occupants about the tire pressure of the vehicle, in some of the vehicles they have separate monitors to constantly display the tire pressure, as a result, it stops them from getting a flat tire ensuring a seamless journey.

Chrysler Pacifica has TPMS integrated on the dashboard.
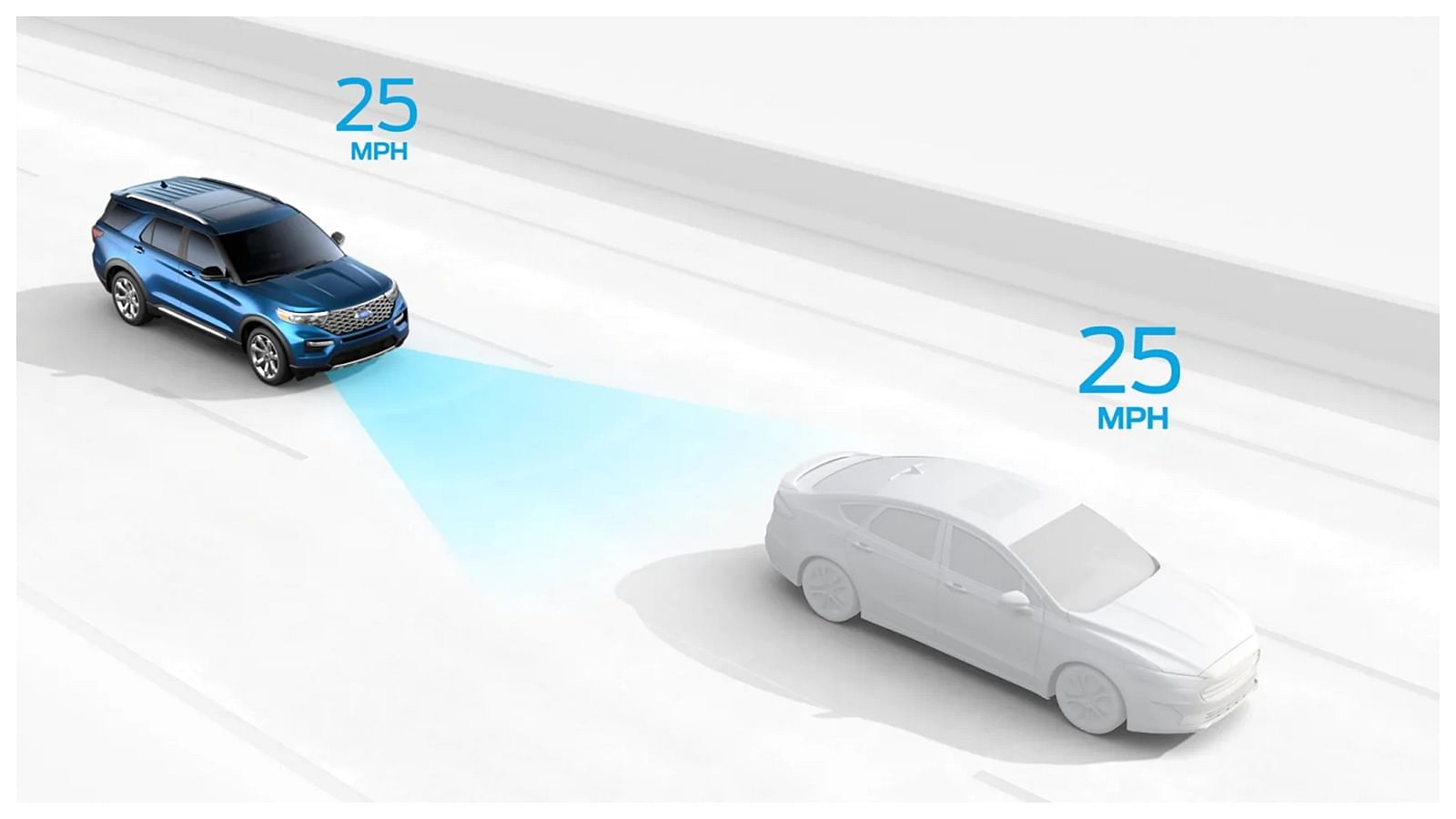
- Adaptive Cruise Control: This system is especially very important for the highway runs, it helps to keep a safe distance from the other vehicles by slowing the vehicle down using sensors, it is way superior to the standard cruise control which only is able to maintain a preset speed. The Adaptive cruise control system also uses a GPS to gauge the terrain and provides the response according to that. Cadillac Escalade’s Supercruise and Ford’s Intelligent Cruise Control are pristine examples of this.

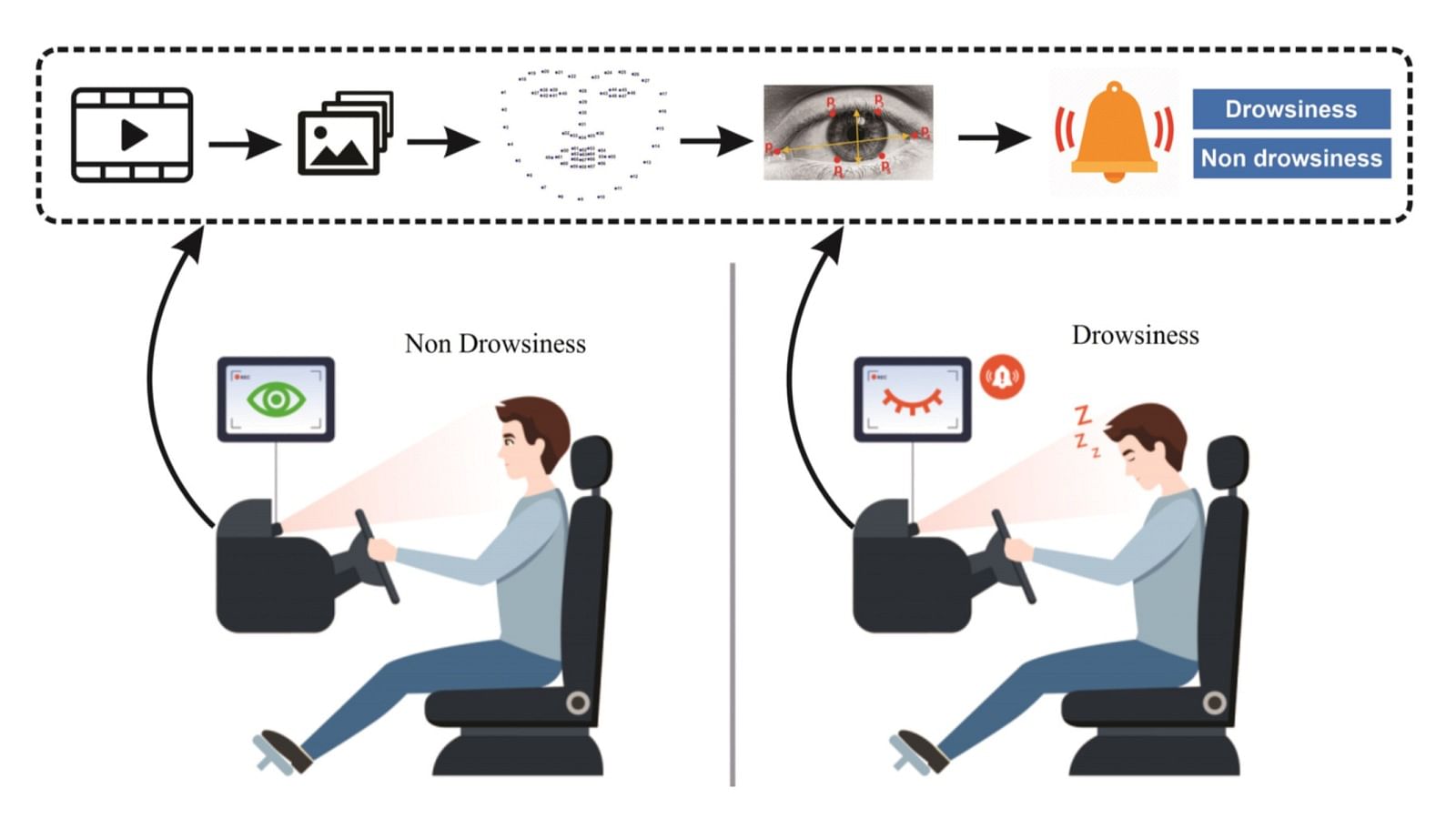
- Driver Drowsiness Detection System: This is an AI-based system that monitors the attention level of the driver using cameras and based on the inputs and feedback provided by him/her according to the changing road conditions and alerts the driver if the driver is found drowsy.
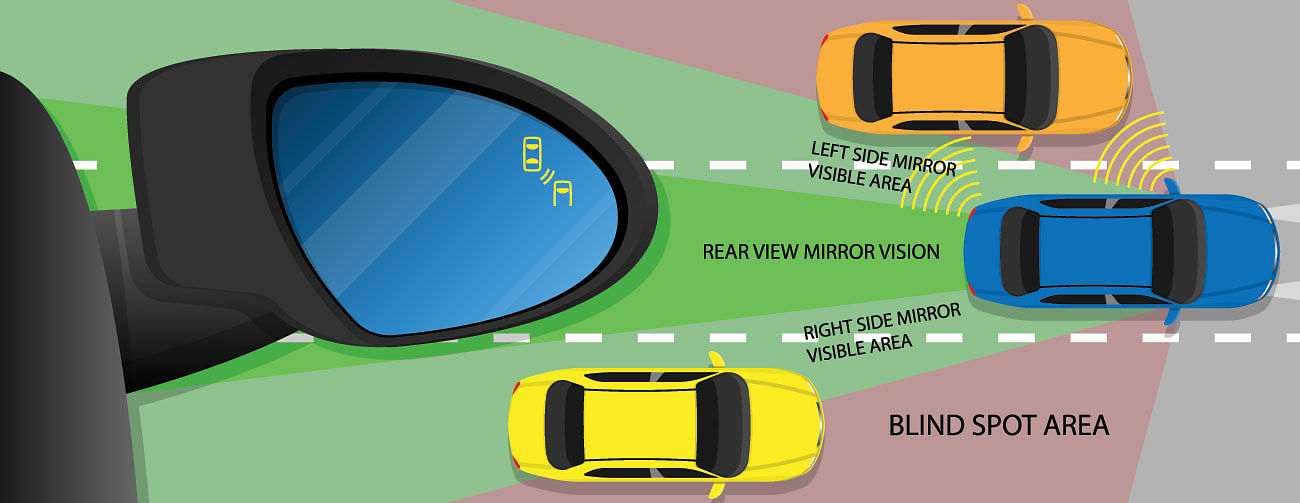
- Blind-Spot Monitoring: This system uses cameras along with radars to increase visibility and reduce the blindspots as a result helps in the avoidance of a collision.
- Rear Cross-Traffic Alert: This is usually paired with the Blind-spot monitoring system which alerts the driver about oncoming traffic by sending signals like the indicator neat the A-pillar or the Indicator on the ORVM

- Forward-Collision Warning: This technology uses radar and cameras to map the road ahead and analyses whether there are any obstacles, pedestrians or other vehicles ahead. It starts by sending alerts to the driver that there might be a collision scenario upfront. It is particularly useful in foggy conditions when visibility is compromised.
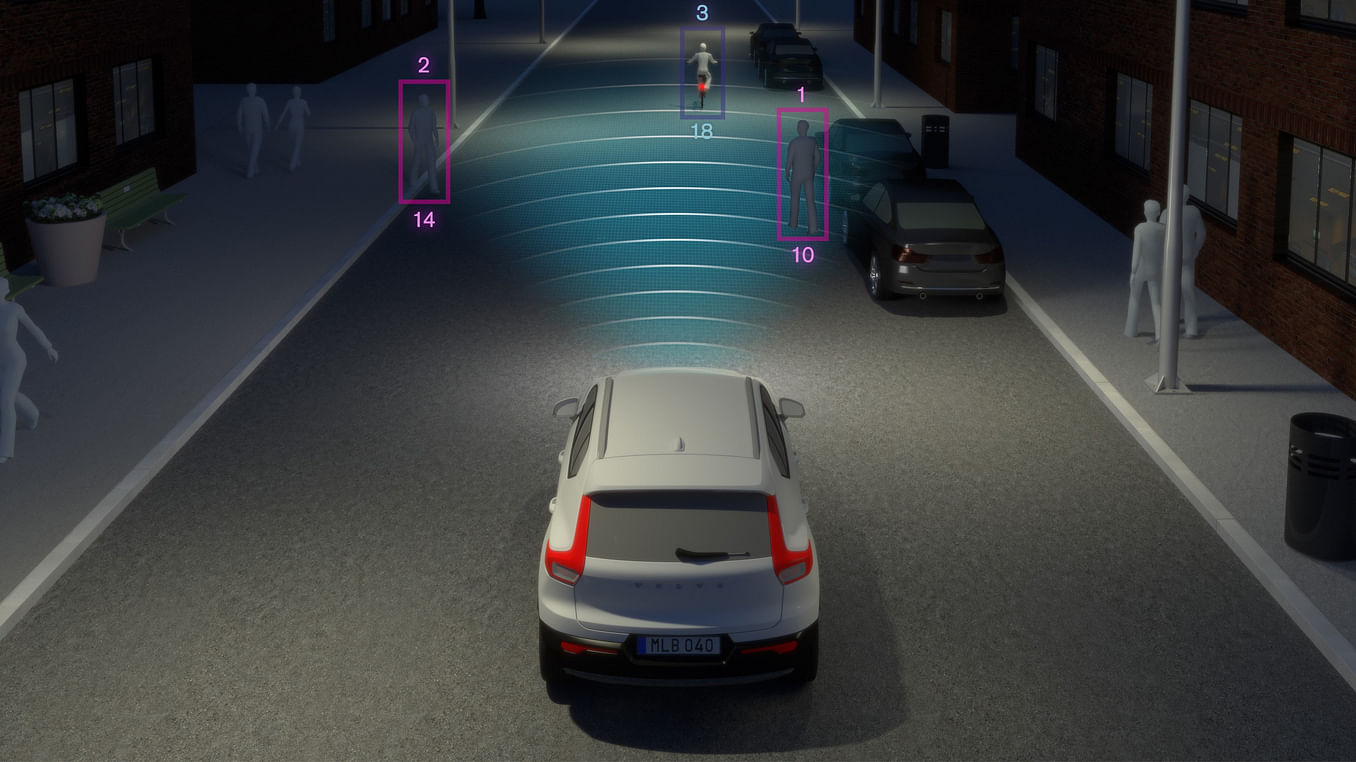
- Automatic Emergency Braking: This system usually assists the Forward collision warning and is a part of the collision avoidance system. This system takes the input from the Forward collision warning system and if the driver has not responded to the warnings then the vehicle automatically deploy the automatic emergency braking system. Volvo is most famous for this, there are multiple videos on the internet of Volvo trucks coming to an abrupt stop after detecting pedestrians.

- Lane-Departure Warning: This is more of a driver aid rather than a safety system, in this the vehicle uses a front camera to judge the lane in which it is traveling and if it moves away, then warning signs are deployed. Most of the time it is coupled with other driver aids.
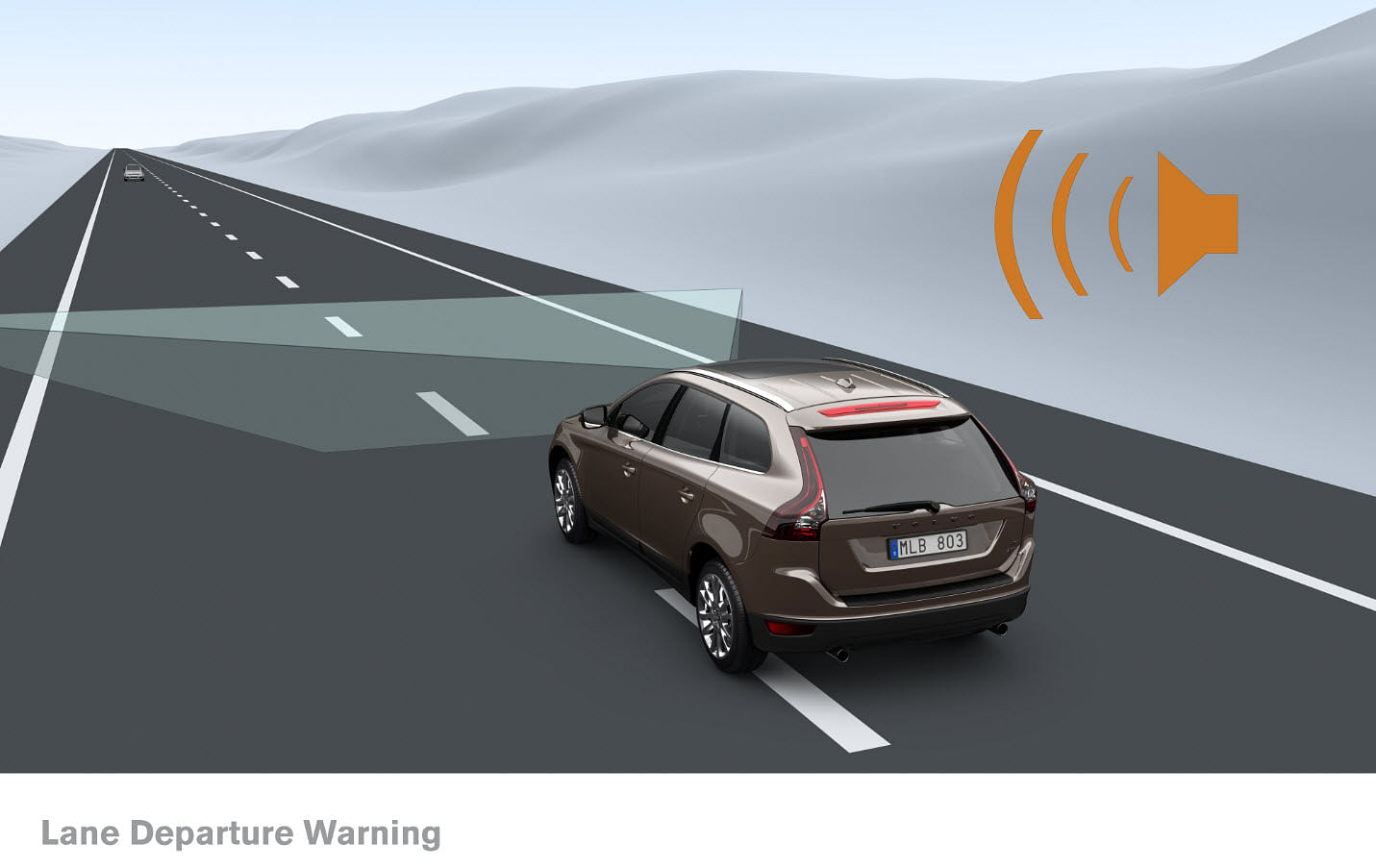
- Lane-Keeping Assist: It is the system that is usually paired with the Lane-Departure warning system in which as soon as the Land departure warning system has floated a warning the vehicle Lane keep assist system will take a corrective measure by providing input to the steering system. There is a more advanced version of this system available as well.
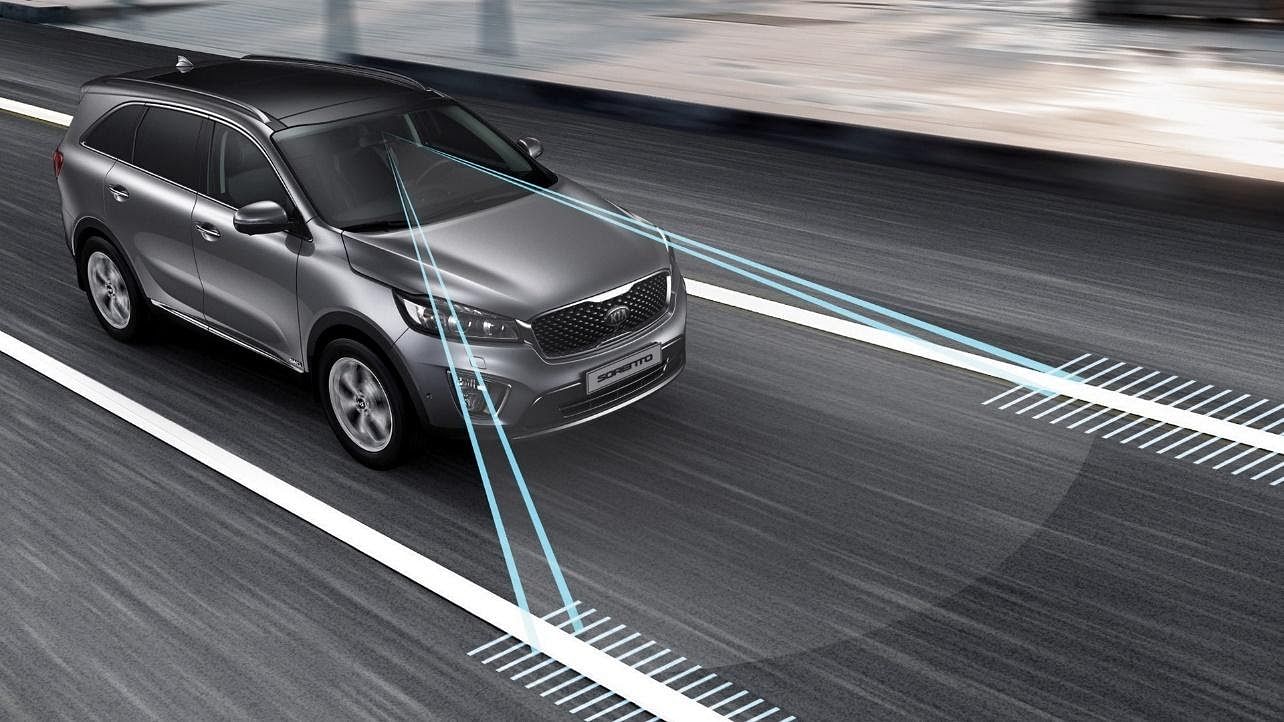

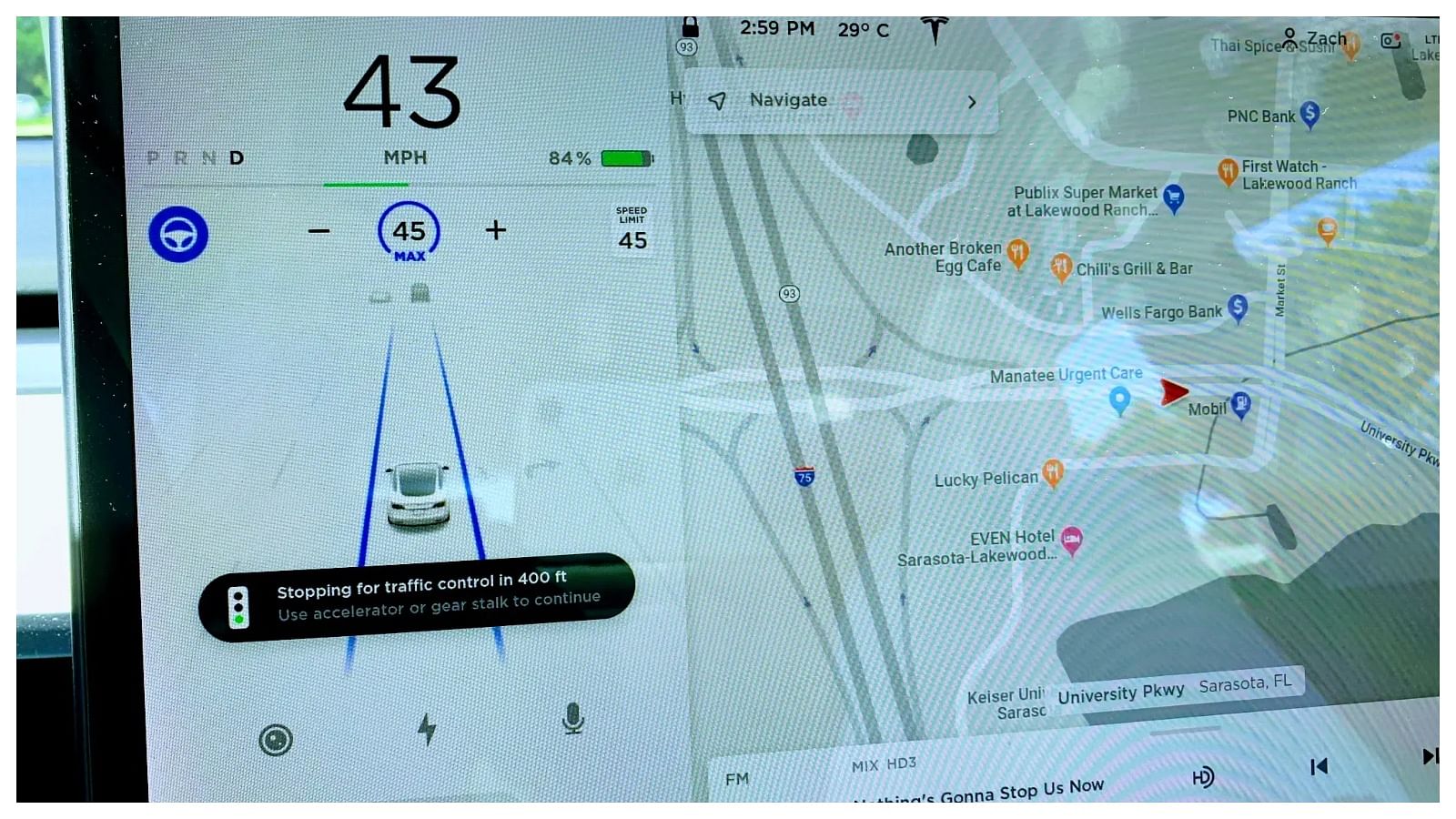
- Lane-Centering Assist: This system is usually the more advanced version of the Lane Keep assist system and is paired with the Adaptive Cruise Control to provide steering feedback to steer the vehicle in the center of the lane. These features really work well in Tesla cars like the Tesla Model S
- Lane-Tracing Assist: Wondering why it is on the list? The fact that this system worlds even when the lane markers are not there, it marks it own track using the camera and the Adaptive Cruise control system.
- Pedestrian Detection: Earlier we discussed the forward collision and avoidance system, the pedestrian detection system is definitely a part of it but in this case, it takes into consideration the pedestrian at the rear as well. Usually paired with the automatic braking system.

- Traffic-Sign Recognition: The last on the list of active safety features is the traffic sign recognition system which works by using cameras. This not only recognizes the stop-and-go signals but also the speed limits as well. This also works with the Adaptive Cruise Control system.
Passive Safety Features:
These are those safety features that are deployed once there are any accidents. These safety features usually prevent loss of life. Here are a list of a few passive safety features:
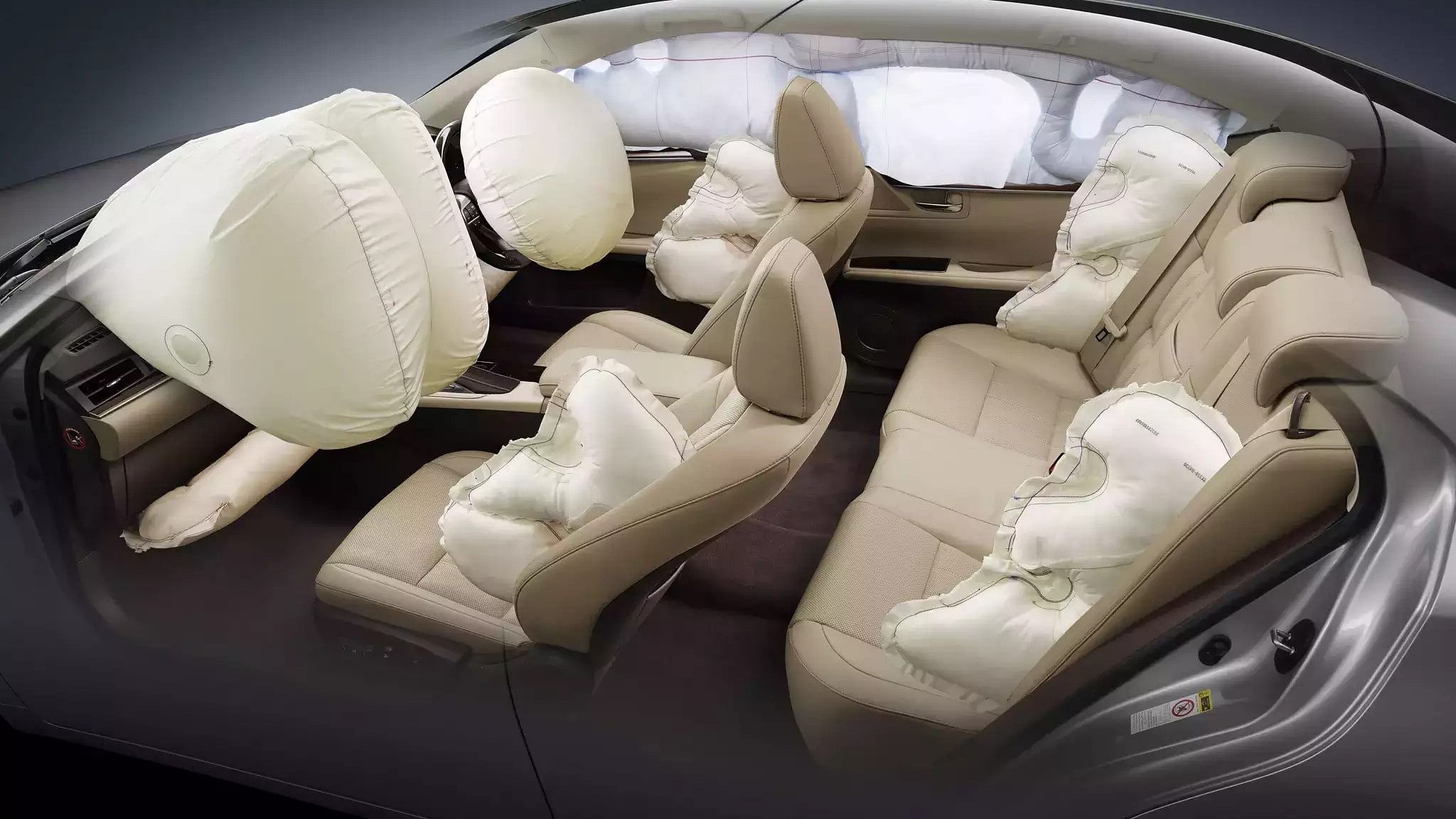
- Airbags: These are sensor-based devices that analyze accident impact and launch airbags that prevent the passenger from the direct impact of the accident. The launching of airbags involves a small controlled explosion which results in the launching of the airbags. The airbags help greatly in case of accidents but it launched without warning may lead to serious injuries. Airbags have been mandatory since 1999.

- Seatbelts: These devices are mandatory safety features that help a passenger to remain in their places during an accident. Seat Belt also saves a passenger and drivers from direct impact. It has been mandatory since 1968.

- Crumble zone and reinforced pillars: These help to maintain the integrity of the cabin structure and minimize the impact on the cabin by absorbing the impact by using the concept of impulse.

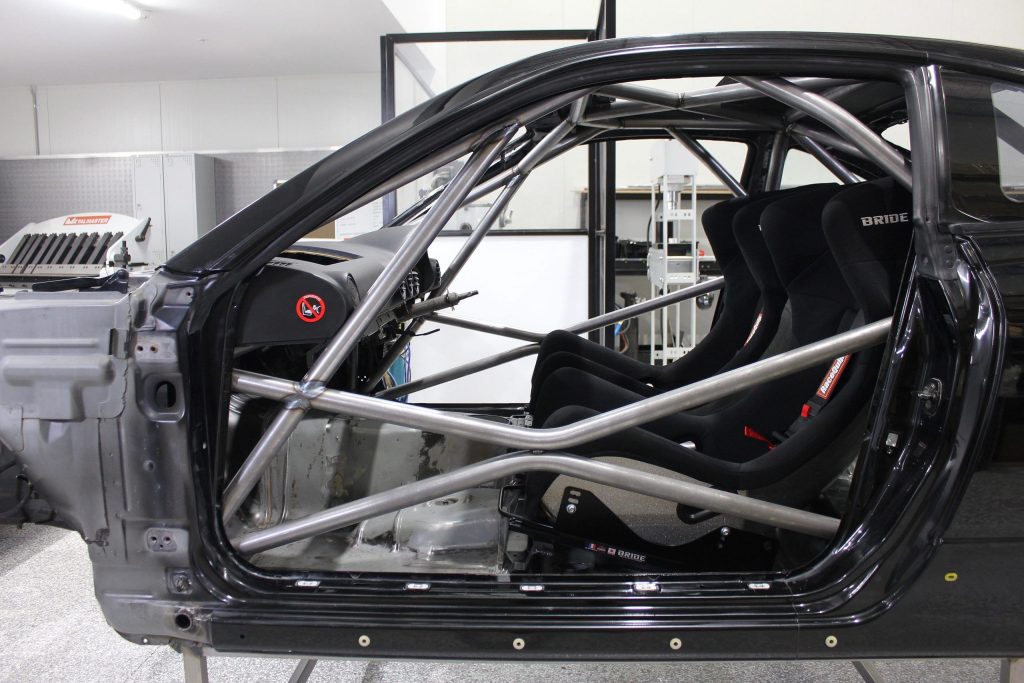
- Roll cages: This helps to keep the roof from crumbling down when the vehicle topples or another vehicle crashes on top of it.

Apart from this list of the safety system, we have some more system that takes safety and convenience to the next level which are listed below:
- Adaptive Headlights and Automatic High beams: This system helps greatly while driving in hilly areas as the adaptive headlights analyze the corners and adjust the light beams accordingly. The Automatic high beams are a boon when it comes to night driving.
- Automatic rain-sensing wipers: This is one of the most common systems nowadays present in many cars where a sensor analyses the need for wipers and deploys them accordingly without input from the driver.
- Parking Systems: Nowadays many vehicles are equipped with a parking system in which the vehicle is able to steer itself into a particular spot without the need for input from the driver. This system uses sensors and cameras to do the maneuver and is a boon, especially while parallel parking.